In today’s digital age, where data is considered the new currency, securing the cloud infrastructure is of paramount importance. Cloud Infrastructure security refers to the measures and technologies put in place to protect the underlying hardware and software components of a cloud environment, from external cyber threats and internal vulnerabilities. With organizations increasingly migrating their operations to the Cloud, the need for robust security practices has become more critical than ever.

Defining the Shared Responsibility Model
The Shared Responsibility Model in cloud security entails that while cloud service providers (CSPs) are responsible for securing their Cloud infrastructure, customers are responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud.
This model highlights the need for organizations to understand their respective roles in securing the cloud environment, and effectively collaborating with their cloud providers to ensure comprehensive security.
Key Cloud Threats and Vulnerabilities
Several common threats and vulnerabilities can compromise the security of your cloud infrastructure.
Several common threats and vulnerabilities can compromise the security of your cloud infrastructure. Data breaches are a major concern, as they can result in the exposure of sensitive information, and damage the reputation of an organization.
Un-authorized access to cloud resources, whether through weak passwords or compromised credentials, can also lead to data leaks and breaches.
Resource hijacking, where cybercriminals exploit cloud resources for their malicious activities, is another significant threat that organizations need to be wary of.
Misconfigurations are one of the most common vulnerabilities in cloud environments, as they can un-intentionally leave systems exposed to attacks.
Insecure APIs, which are commonly used to interact with cloud services, can also be exploited by cybercriminals to gain un-authorized access.
Insider threats, whether intentional or accidental, also pose a significant risk to cloud security.
Best Practices for Securing Your Cloud Infrastructure
To protect the cloud infrastructure from these external threats and internal vulnerabilities, it is essential to implement best practices for cloud robust security.
Some of those good practices include:
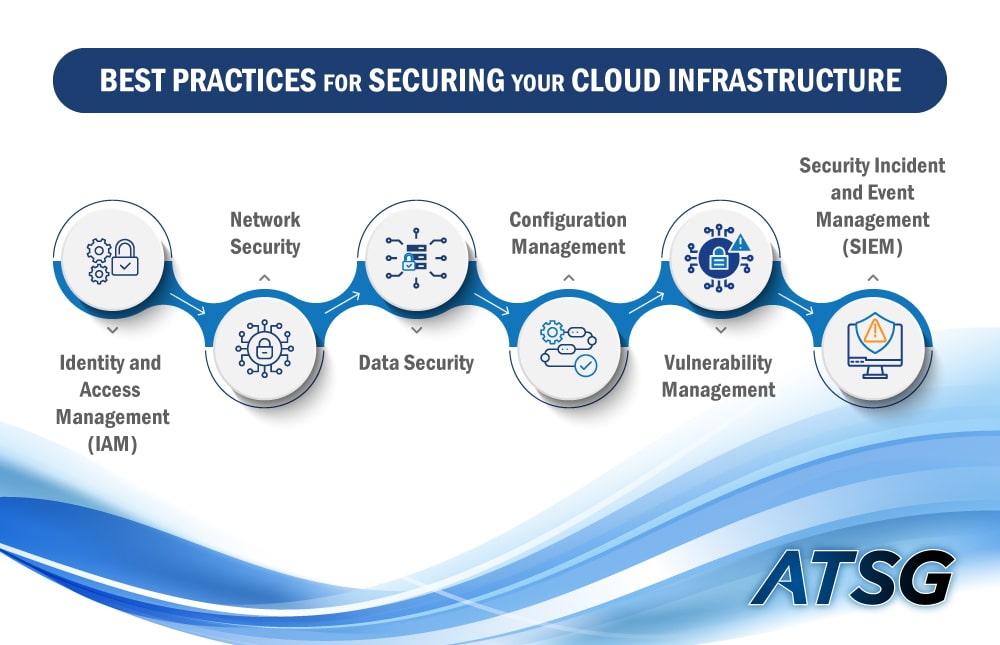
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implement robust IAM solutions that include multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least privilege access controls, to ensure that only authorized users can access your cloud resources.
Network Security
Utilize firewalls, intrusion detection / prevention systems (IDS / IPS), and secure network configurations to monitor and control the traffic flowing in and out of the cloud environment.
Data Security
Employ strong encryption practices for data at rest and in transit, to protect your data from un-authorized access. Implement data loss prevention (DLP) solutions to prevent the accidental or intentional destruction of sensitive information or data.
Configuration Management
Implement Artificial Intelligence (AI) powered automation tools and continuous monitoring, to ensure that your cloud configurations are secure and compliant with industry standards.
Vulnerability Management
Conduct regular vulnerability scanning and patching processes, to identify and remediate any weaknesses in your cloud environment. This needs to be an on-going process.
Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM)
Utilize SIEM tools for centralized log aggregation and threat detection, to effectively monitor and respond to security incidents in real time. This will result in a well structured approach to deal with cybersecurity incidents.
The Role of Cloud Provider in Shared Responsibility
Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) play a crucial role in securing the underlying Cloud infrastructure, including physical servers, networking equipment, and hypervisors. However, customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, identities, and access within the cloud environment.
Organizations need to understand the security aspects handled by their cloud provider, and take proactive measures to secure their assets within the Cloud. The responsibilities of both the CSP, and the cloud tenant need to be clearly defined in the Service Level Agreement (SLA).
The Cybersecurity Capabilities of ATSG
As a leading global provider of Managed IT Services and cutting edge Cybersecurity solutions, ATSG is committed to providing top-notch capabilities for effectively securing on-premise and cloud environments.
Our well-rounded cybersecurity solutions include Advisory & Assessment services, Managed Detection & Response (MDR), Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR), and Extended Detection & Response (XDR). ATSG understands that every organization has unique needs, and to address those, we offer customized cybersecurity solutions.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, implementing robust mechanisms is crucial. This includes advanced threat detection and response mechanisms, such as Extended Detection & Response (XDR).
ATSG’s XDR solutions provide unified threat monitoring, detection, and response capabilities across the network, endpoints, data, and applications, ensuring comprehensive security coverage for the cloud environment.
By implementing best practices for securing your cloud infrastructure, and collaborating effectively with your cloud service provider (CSP), you can mitigate the risks posed by cyber threats.
Contact ATSG for highly secure Cloud Computing solutions and services for your organization. Our Cybersecurity solutions portfolio spans across Cyber Risk Advisory and Assessment, MDR, EDR, and XDR, delivering full-stack security capabilities under one roof.




